What is Autonomous Driving, Self-Driving Cars or Autopilot?
Get an in-depth understanding of what autonomous driving, self-driving cars and autopilot technology mean through this comprehensive blog post.

Autonomous driving, self-driving cars and autopilot technology are all terms used to describe the same concept: vehicles that can drive themselves, without human intervention. In this article, we'll explore the differences between these three terms and what they mean for the future of driving.
Defining Autonomous Driving, Self-Driving Cars and Autopilot Technologies
Autonomous driving is a broad term used to describe cars or other vehicles that use sensors, cameras, and artificial intelligence (AI) to navigate roads and obstacles without the need for human input. This technology relies on a combination of sensors, cameras, and machine learning algorithms to perceive and respond to the environment around the vehicle. Autopilot systems can detect other vehicles, pedestrians, and road markings, and can adjust the speed and direction of the vehicle accordingly.
Self-driving cars are a type of autonomous vehicle that has advanced features such as lane guidance and distance sensors. Finally, autopilot technology refers to the ability of a vehicle to autonomously control its direction while following predetermined routes or parameters set by the driver. Autopilot systems can detect other vehicles, pedestrians, and road markings, and can adjust the speed and direction of the vehicle accordingly.
Levels of Autonomy
There are different levels of autonomy in vehicles, ranging from level 1 (driver assistance) to level 5 (full autonomy). At level 1, the driver still has primary control of the vehicle, while at level 5, the vehicle can operate completely independently without any human intervention.
While autonomous driving technology is still in the early stages of development, several automakers, including Tesla, Waymo, and GM, are investing heavily in this area. The potential benefits of autonomous driving include improved safety, reduced traffic congestion, and increased efficiency. However, there are also concerns around issues such as cybersecurity, liability, and the potential impact on employment in the transportation sector.
There are six levels of autonomy in autonomous driving, as defined by the Society of Automotive Engineers (SAE), each with a different level of human involvement required:
- Level 0: No Automation - The driver has full control of the vehicle at all times, with no assistance from automation.
- Level 1: Driver Assistance - The vehicle includes some driver assistance features, such as adaptive cruise control or lane-keeping assistance. However, the driver still has primary control of the vehicle.
- Level 2: Partial Automation - The vehicle can control steering, acceleration, and braking under certain circumstances, but the driver must still monitor the vehicle and be ready to take control at any time.
- Level 3: Conditional Automation - The vehicle can handle most aspects of driving under certain conditions, such as on a highway, but the driver must still be available to take control if necessary.
- Level 4: High Automation - The vehicle is capable of driving itself in most situations, but may require driver intervention in certain circumstances.
- Level 5: Full Automation - The vehicle is capable of completely autonomous driving, with no human input required at any time.
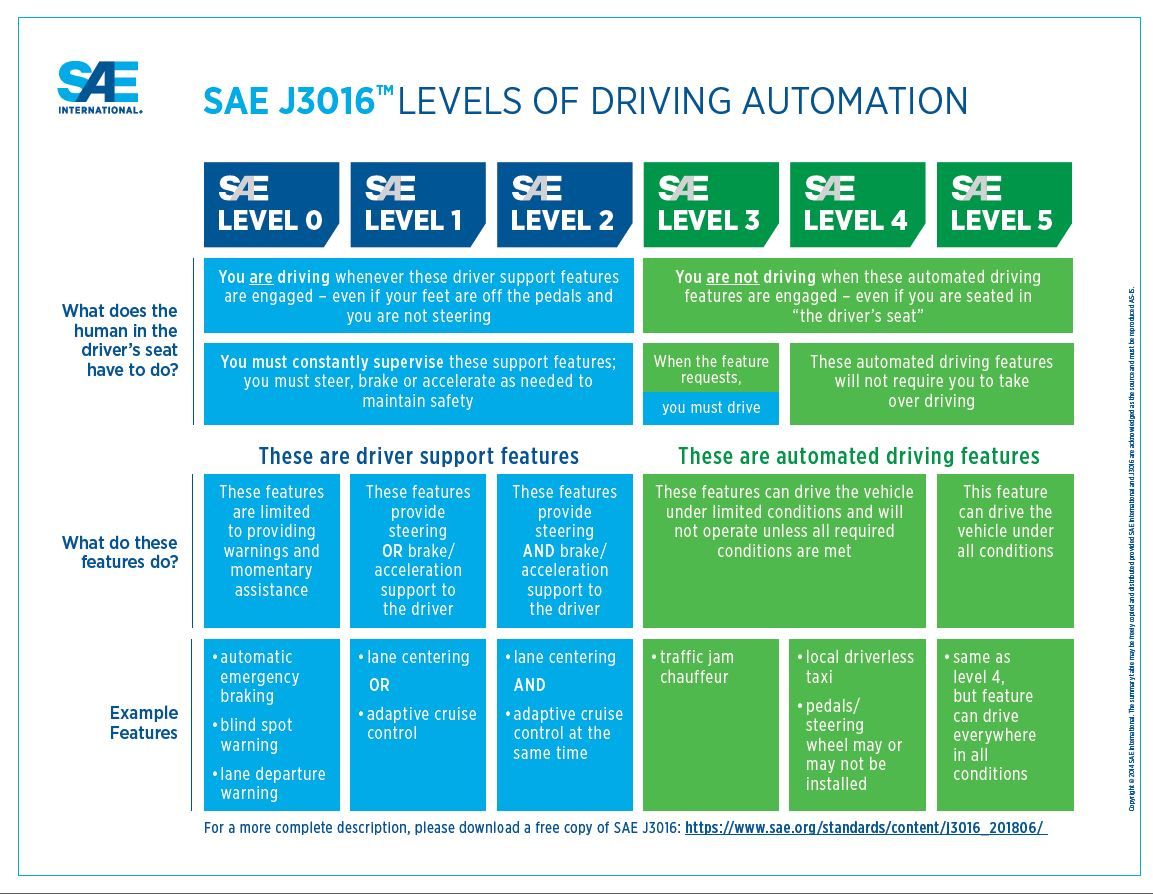
Source: SAE International
Although some automakers have aspirations for level 5 autonomous vehicles, the majority of them are level 2 or level 3 today. Level 4 and level 5 autonomous vehicle development is still ongoing, and many technological, legal, and societal issues need to be resolved before these vehicles can be made generally accessible.
Level Implementation
Here is where we stand as of the day this post is published on which automaker deployed autonomous levels.
- Mercedes-Benz EQS and Mercedes-Benz S-Class are the only cars currently available with SAE Level 3 autonomous driving technology. This technology allows for some dynamic driving tasks to be handled by the car, such as speed and steering, but a driver must still be present and ready to take over if necessary. Mercedes-Benz is the first automaker to receive government approval in the US for a Level 3 driving feature. This feature is currently only available in Nevada, and allows for conditional hands-free driving.
- Tesla's Full Self-Driving package provides a unique driving experience that is technically an SAE Level 2 system.
- Honda has also announced plans to develop technology enabling its level 3 self-driving capability to function at any speed below legal limits on highways.
- Level 4 autonomy are in development but not yet available on the market.
- Level 5 full self-driving capabilities are not expected to be available for years.
Mercedes-Benz says it has achieved Level 3 automation, which requires less driver input, surpassing the self-driving capabilities of Tesla and other major US automakers
https://www.businessinsider.com/mercedes-benz-drive-pilot-surpasses-teslas-autonomous-driving-system-level-2023-1
Tesla has issued a recall of all 362,758 vehicles equipped with its Full Self-Driving (FSD) Beta software in the US due to safety risks. The recall covers 2016-2023 Model S and Model X vehicles, 2017-2023 Model 3, and 2020-2023 Model Y vehicles equipped with FSD Beta software or pending installation.
Tesla will attempt to fix the FSD feature through an over-the-air software update. The company has identified 18 reports of incidents between May 8, 2019, and September 12, 2022 that may be related to the conditions described in the recall notice.
The recall comes after NHTSA raised its issue with Tesla about FSD Beta on January 25, 2023. Tesla met with regulators on several occasions until February 7 when it decided to administer a voluntary recall out of an abundance of caution.
CEO Elon Musk has objected to the use of the term "recall" for an over-the-air software update, tweeting that it is "anachronistic and just flat wrong!".
How Autonomous Cars Work
Autonomous cars are equipped with various sensors and cameras which enable them to detect objects in their environment and react accordingly. As the car moves, radar and LIDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) sensors measure the distance of nearby objects while seven or more stereo cameras capture high-resolution visuals. This information is then analyzed by onboard computers which use complex algorithms to enable the vehicle to perceive its surroundings. The data collected helps the car make decisions regarding its route, speed, braking, and other driving variables. Some of the core components, and how they work.
- Perception: Autonomous cars use sensors and cameras to detect their surroundings, including other vehicles, pedestrians, and objects. They use a combination of radar, LIDAR, and computer vision to create a 3D model of the environment in real-time.
- Mapping: Autonomous cars use detailed maps to help them navigate, with the maps being stored in the car's onboard computer. These maps include information such as lane markings, traffic lights, and road signs.
- Decision-Making: Once the car has perceived its environment and analyzed the information from the maps, the car's onboard computer makes decisions on how to respond. The computer uses algorithms to analyze the data and determine the best course of action, such as adjusting speed or making a turn.
- Control: The car's control systems then execute the decisions made by the computer. The car's steering, acceleration, and braking are all controlled by computer systems.
- Learning: Autonomous cars use machine learning algorithms to continually improve their driving performance. They can analyze their driving data to learn from past experiences and adapt to different driving conditions.
Autonomous driving technology, which is still in development, has the potential to improve safety and traffic flow if developed and applied properly.
Photo by Obi - @pixel7propix / Unsplash

Benefits of Autonomous Driving Technology
Autonomous driving technology has the potential to dramatically reduce car accidents, as well as save lives. Thanks to AI and algorithms, self-driving cars are able to quickly detect hazards and adjust their speed or route accordingly. This technology can also decrease traffic congestion by automatically controlling vehicles and keeping them a safe distance apart from each other. Additionally, autonomous vehicles have the potential to significantly improve comfort and convenience for drivers and passengers alike, allowing them to enjoy a more leisurely ride without having to constantly monitor the road.
Where Can I Test Drive Autonomous Cars?
You can get behind the wheel of a self-driving vehicle in certain regions around the world, although this may depend on local laws and regulations. For example, California has allowed autonomous vehicles to be tested on public roads since 2014. Additionally, some car manufacturers have set up testing sites specifically for their vehicles. Other companies offer demonstrations of different features at events or conferences, allowing the public to experience self-driving cars without having to actually drive them.
Regulations for Autonomous Car Development and Deployment
Autonomous car development and deployment is subject to regulations set by local governments. Currently, there is no single body responsible for the regulation of autonomous vehicle technology globally, although the UN has formed a working group to better understand the potential effects of self-driving cars. National and local governments are responsible for regulating the use, manufacturing and sale of autonomous vehicles, as well as setting out any driving or programming rules that should be adhered to. Generally speaking, autnonomous car manufacturers are expected to ensure the safety of their vehicles before they are released on public roads.
Best 10 autonomous vehicle experiences
As of now, fully autonomous cars are not yet available for purchase, but some car manufacturers have released semi-autonomous features that provide a glimpse of what the future of autonomous driving may hold. Here are ten of the best autonomous car experiences available today:
- Tesla Autopilot: Tesla's Autopilot feature offers a range of semi-autonomous driving features, including automatic lane centering, adaptive cruise control, and automatic parking.
- Mercedes-Benz Drive Pilot: Mercedes-Benz's Drive Pilot system offers similar features to Tesla's Autopilot, with automatic lane centering and adaptive cruise control.
- Cadillac Super Cruise: Cadillac's Super Cruise system allows for hands-free driving on compatible highways, with automatic lane centering and adaptive cruise control.
- Audi Traffic Jam Pilot: Audi's Traffic Jam Pilot system allows for hands-free driving in congested traffic at low speeds.
- Volvo Pilot Assist: Volvo's Pilot Assist system offers automatic steering and adaptive cruise control on compatible roads.
- BMW Driving Assistant Plus: BMW's Driving Assistant Plus system offers automatic lane centering, adaptive cruise control, and automatic parking.
- Nissan ProPilot Assist: Nissan's ProPilot Assist system offers automatic steering, adaptive cruise control, and lane centering on compatible roads.
- Ford Co-Pilot360: Ford's Co-Pilot360 system offers automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and adaptive cruise control.
- Subaru EyeSight: Subaru's EyeSight system offers automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and adaptive cruise control.
- Hyundai SmartSense: Hyundai's SmartSense system offers automatic emergency braking, lane-keeping assistance, and adaptive cruise control.
Photo by Tesla Fans Schweiz / Unsplash
Although the technology is still in its infancy, there are currently a number of examples of semi-autonomous driving capabilities that enhance road safety and convenience. We can anticipate increasingly totally automated driving experiences in the future as technology develops.
Pros & Cons
Autonomous driving technology has the potential to offer several benefits, but it also comes with certain drawbacks. Some of the pros and cons of autonomous driving cars are discussed below -
Pros:
- Increased Safety: Autonomous driving technology can reduce the risk of accidents caused by human error, such as distracted driving, speeding, and impaired driving.
- Improved Traffic Flow: Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other to optimize traffic flow and reduce congestion on roads.
- Increased Mobility: Autonomous vehicles can offer greater mobility for people who are unable to drive due to age, disability, or other reasons.
- Enhanced Convenience: Autonomous vehicles can allow passengers to use their time more efficiently by working, reading, or relaxing while on the road.
- Reduced Energy Consumption: Autonomous vehicles can optimize acceleration and braking patterns to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
Photo by Jason Blackeye / Unsplash
Cons:
- High Cost: Autonomous driving technology can be expensive, which can make the vehicles themselves more expensive and limit their accessibility.
- Job Losses: Autonomous vehicles have the potential to replace drivers in certain industries, such as transportation and delivery, which could lead to job losses.
- Cybersecurity Risks: Autonomous vehicles rely heavily on software and internet connectivity, which can make them vulnerable to hacking and cyber attacks.
- Legal and Regulatory Issues: The legal and regulatory framework for autonomous driving is still in development, which can lead to uncertainty and potential liability issues.
- Ethical Concerns: Autonomous vehicles may face difficult ethical decisions, such as how to respond to a situation where there is no clear "right" answer, such as a situation where an accident is unavoidable.
While self-driving technology is still in its early stages of development, it is critical to weigh the potential benefits and drawbacks of this technology as it evolves.
Future
Autonomous driving has the potential to revolutionize the way we move people and goods, with potential impacts across a wide range of industries. Here are some of the potential impacts of autonomous driving in the future:
- Improved Safety: Autonomous driving technology can reduce the number of accidents caused by human error, potentially saving thousands of lives each year.
- Reduced Traffic Congestion: Autonomous vehicles can communicate with each other and optimize traffic flow to reduce congestion on roads, saving time and fuel for all drivers.
- Increased Efficiency: Autonomous vehicles can optimize acceleration and braking patterns to reduce fuel consumption and carbon emissions.
- Greater Accessibility: Autonomous vehicles can offer greater mobility for people who are unable to drive due to age, disability, or other reasons.
- Reduced Need for Parking: Autonomous vehicles can be used for ride-sharing and other on-demand services, reducing the need for parking spaces in urban areas.
- New Business Models: Autonomous driving technology can enable new business models, such as on-demand transportation services and delivery services that operate around the clock.
- Improved Urban Planning: Autonomous vehicles can reduce the need for wide roads and parking spaces, potentially enabling more compact and efficient urban planning.
Photo by Emile Guillemot / Unsplash
Conclusion
Autonomous driving technology has come a long way since its inception, with early experiments dating back to the 1920s. Today, we have cars on the roads that can drive themselves under certain conditions, with some models offering features like lane-keeping assistance, adaptive cruise control, and automated parking. While the technology is still in the early stages of development, it has the potential to revolutionize the transportation industry, with benefits such as improved safety, increased efficiency, and reduced traffic congestion.
However, there are also many challenges that need to be addressed before autonomous driving can become more widespread. These challenges include technical issues such as sensor reliability and cybersecurity, legal and regulatory issues around liability and insurance, and societal issues such as job losses and ethical concerns.
Despite these challenges, many automakers and technology companies are investing heavily in autonomous driving technology, with some predicting that we may see fully autonomous vehicles on the roads within the next few decades. It remains to be seen how quickly the technology will develop and how it will be adopted by consumers and businesses, but it is clear that the future of transportation is likely to be significantly impacted by the continued evolution of autonomous driving technology.






